Using Ships as a Dungeon, Part 3
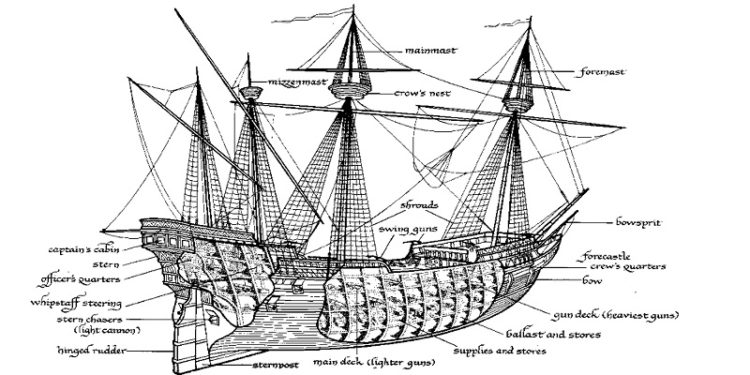
Last time we examined ship purposes, ship based plots, and ship quirks. This time we’ll look at the different parts of the ship, a ship template, and water hazard examples.
Ship Related Words
- Abaft: toward or at the stern of a ship; further aft
- Affreightment: hiring of a vessel
- Aft: in or toward the back part of a ship or airplane
- Afterdeck: deck behind a ship’s bridge
- Afterguard: men who work the aft sails on the quarterdeck and poop deck
- Ahull: with sails furled and helm lashed to the lee-side
- Amidships: in the middle part of a ship
- Astern: at the stern of a ship
- Backstay: stay extending from ship’s mastheads to the side of the ship
- Ballaster: one who supplies ships with ballast
- Bargemaster: owner of a barge
- Bay: an area in an airplane or a ship that is used for carrying goods or equipment
- Beam: the widest part of a ship from one side to the other
- Bee: hardwood on either side of bowsprit through which forestays are reeved
- Belay: to secure a rope by winding on a pin or cleat
- Berth: a bed on a train or ship
- Bilge: the bottom part of a boat
- Binnacle: case in which a ship’s compass is kept
- Bitts: posts mounted on a ship for fastening ropes
- Blade: one of the flat parts of a propeller that spins around and pushes a boat or airplane forward
- Bluepeter: blue flag with a white square in center used as ship’s signal
- Boatswain (bosun): ship’s crewmember in charge of equipment and maintenance
- Bobstay: rope used on ships to steady the bowsprit
- Bollard: short post on a wharf or ship to which ropes are tied
- Boltrope: strong rope stitched to edges of a sail
- Boom: a long pole fixed to the bottom of a boat’s sail, that is used for changing the direction of the sail
- Bottomry using the ship as collateral to finance a sea voyage
- Bow: front of a ship
- Bower: anchor carried at bow of a ship
 Bowline: rope used to keep weather edge of a sail taut
Bowline: rope used to keep weather edge of a sail taut- Bowsprit: a long pole (spar) that sticks out from the front of a ship
- Brails: ropes on edge of sail for hauling up
- Bream: to clean a ship’s bottom by burning off seaweed
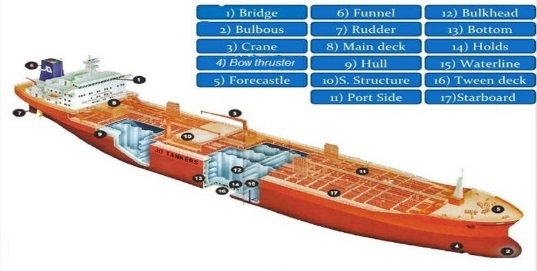
- Bridge: the part of a ship from which it is controlled
- Brig: a place on a ship where prisoners are kept
- Bulwark(s): the side of a ship above the deck
- Bumpkin: spar projecting from stern of ship
- Bunt: middle of sail, fish-net or cloth when slack
- Buntline: rope attached to middle of square sail to haul it up to the yard
- Burgee: small ship’s flag used for identification or signaling
- Cabin: a private room on a ship for a passenger or one of the people working on the ship
- Cable: heavy rope or chain for mooring a ship
- Cabotage: shipping and sailing between points in the same country
- Camber: slight arch or convexity to a beam or deck of a ship
- Capstan: upright device for winding in heavy ropes or cables, especially on a ship or at a port
- Careen: to turn a ship on its side in order to clean or repair it
- Catapult: a piece of equipment on a ship used for sending aircraft into the air
- Cathead: projection near the bow of a ship to which anchor is secured
- Chine: the intersection of the middle and sides of a boat
- Chock: metal casting with curved arms for passing ropes for mooring ship
- Cleat: a metal object that you tie a rope around in order to fasten something in place, especially on a ship
- Clew: corner of sail with hole to attach ropes
- Coaming: raised edge around ship’s hatches to keep water out
- Cocket: official shipping seal; customs clearance form
- Cockpit: the part of a boat where the controls are
- Cofferdam: narrow vacant space between two bulkheads of a ship
- Companionway: stairs from upper deck of ship to lower deck
- Conning: tower the part on top of a submarine from which the periscope sticks out
- Cordage: ropes in the rigging of a ship
- Cringle: loop at corner of sail to which a line is attached
- Crosstrees: horizontal crosspieces at a masthead used to support ship’s mast
- Crow’s nest: a place near the top of a ship’s mast where a sailor stands to look out over the ocean
- Davit: device for hoisting and lowering a boat
- Deadeye: rounded wooden block with hole used to set up ship’s stays
- Deadwood: timbers built into ends of ship when too narrow to permit framing
- Deck: one of the levels on a ship, train, or stadium
- Demurrage: delay of vessel’s departure or loading with cargo
- Dodger: shield against rain or spray on a ship’s bridge
- Dogwatch: a short, evening period of watch duty on a ship
- Downhaul: rope for holding down or hauling down a sail or spar
- Dyogram: ship’s chart indicating compass deflection due to ship’s iron
- Earing: line for fastening corner of a sail to the gaff or yard
- Ensign: large naval flag
- Escape hatch: a small door for escaping from a ship, aircraft, or submarine in an emergency
 Escutcheon part of ship’s stern where name is displayed
Escutcheon part of ship’s stern where name is displayed- Fairlead: ring through which rope is led to change its direction without friction
- Fardage: wood placed in bottom of ship to keep cargo dry
- Fender: a piece of rope or a tire that protects the side of a boat from knocks
- Fiddley: iron framework around hatchway opening
- Figurehead: a wooden model of a person attached to the front of an old-fashioned ship
- Flagstaff: flag pole at stern of a ship
- Flight deck: the open area on a large ship where aircraft can take off and land
- Fluke: part of an anchor that fastens in the ground
- Forebitt: post for fastening cables at a ship’s foremast
- Forecabin: cabin in fore part of ship
- Forecastle (fo’c’sle): the front part of a ship, under the main deck
- Forefoot: foremost end of ship’s keel
- Foremast: mast nearest the bow of a ship
- Foresail: lowest sail set on the foremast of square-rigged ship
- Forestay: stay leading from the foremast to the bow of a ship
- Frap: to draw a sail tight with ropes or cables
- Freeboard: distance between waterline and main deck of a ship
- Funnel (smokestack): a tube that lets out smoke and steam from the engine of a boat or old-fashioned train
- Futtock: rib of a ship
- Gaff: spar on which head of fore-and-aft sail is extended
- Gaff-topsail: triangular topsail with its foot extended upon the gaff
- Galley: the kitchen on a boat or airplane
- Gangplank: a long narrow board that you put between a boat and the land, or between two boats, so that you can walk across
- Gangway: a flat board or metal structure that can be put in place between a ship and land to let people get off or on the ship
- Garboard: plank on a ship’s bottom next to the keel
- Genoa: large jib that overlaps the mainsail
- Grapnel: small anchor used for dragging or grappling
- Groundage: a charge on a ship in port
- Gudgeon: metal socket into which the pintle of a boat’s rudder fits
- Gunnage: number of guns carried on a warship
- Gunwale (singular gunnel): the upper edge of the side of a boat or ship
- Gybe: to swing a sail from one side to another
- Halyard: rope or tackle for hoisting and lowering sails
- Hank: series of rings or clips for attaching a jib or staysail to a stay
- Hawse: distance between ship’s bow and its anchor
- Hawsehole: hole for ship’s cable
- Hawser: large rope for mooring or towing a ship
- Headsail: sail set forward of the foremast of a ship
- Helm: a wheel or handle used for making a boat go in the direction you want
- Hold: the area in an airplane or ship that is used for goods, vehicles, or suitcases
- Holystone: sandstone material used to scrape ships’ decks
- Hull: the part of a ship or boat that floats on the water.
- Hydrofoil: one of the wing-shaped pieces attached to the bottom of a hydrofoil
- Inboard: inside the line of a ship’s bulwarks or hull
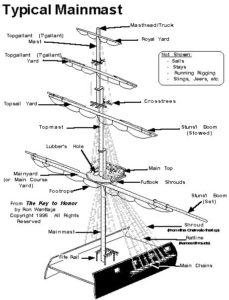 Jack: ship’s flag flown from jack-staff at bow of vessel
Jack: ship’s flag flown from jack-staff at bow of vessel- Jack-block: pulley system for raising topgallant masts
- Jack-cross-tree: single iron cross-tree at head of a topgallant mast
- Jackstaff: short staff at ship’s bow from which the jack is hoisted
- Jackstay: iron or wooden bar running along yard of ship to which sails fastened
- Jackyard: spar used to spread the foot of a gaff-topsail
- Jib: small triangular sail extending from the head of the foremast
- Jibboom: spar forming an extension of the bowsprit
- Jibe: to change a ship’s course to make the boom shift sides
- Jurymast: mast erected on ship in place of one lost
- Kedge: small anchor to keep a ship steady
- Keel: a long thin piece of wood or metal along the bottom of a boat that helps it to balance in the water
- Keelhaul: to punish by dragging under keel of ship
- Keelson: lengthwise wooden or steel beam in ship for bearing stress
- Kentledge: pig-iron used as ballast in ship’s hold
- Lagan: cargo jettisoned from ship but marked by buoys for recovery
- Lanyard: a short rope used on ships for fastening things such as the sails
- Lastage: room for stowing goods in a ship
- Lateen: triangular sail rigged on ship’s spar
- Laveer: to sail against the wind
- Lazaret: space in ship between decks used for storage
- Leeboard: wood or metal planes attached to hull to prevent leeway
- Leech: a vertical edge of a square sail
- Loxodograph: device used to record ship’s travels
- Luff: windward side of a ship; forward edge of fore-and-aft sail
- Lugsail: four-sided sail bent to an obliquely hanging yard
- Lutchet: fitting on ship’s deck to allow mast to pivot to pass under bridges
- Mainmast: sailing ship’s principal mast
- Mainsail: principal sail on a ship’s mainmast
- Mainsheet: rope by which mainsail is trimmed and secured
- Mainstay: stay that extends from the main-top to the foot of the foremast
- Manrope: rope used as a handrail on a ship
- Martingale: lower stay of rope used to sustain strain of the forestays
- Mast: a tall pole that the sails hang from on a ship. The masthead is the top of the mast
- Mizzen: the mast that holds the mizzen sail or the sail behind the main sail on a ship
- Mizzenmast: mast aft or next aft of the mainmast in a ship
- Moonraker: topmost sail of a ship, above the skyscraper
- Muster: station a place, especially on a ship, where people should gather if there is an emergency
- Oakum: old ropes untwisted for caulking the seams of ships
- Oarlock: American the piece of metal that holds the oar of a boat
- Orlop: lowest deck in a ship having four or more decks
- Outhaul: rope used to haul a sail taut along a spar
- Outrigger: spar extended from side of ship to help secure mast and helps it to float
- Paddle: one of the long flat boards that are joined together in the shape of a wheel, used for moving a paddle boat through the water
- Painter: a rope attached to the front of a boat and used for tying it to something such as a post
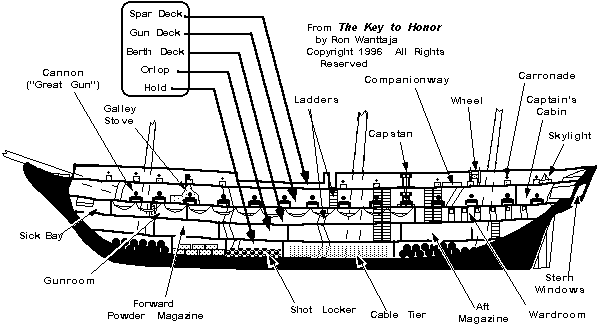 Pallograph: instrument measuring ship’s vibration
Pallograph: instrument measuring ship’s vibration- Parrel: band by which a yard is fastened to a mast
- Patroon: captain of a ship; coxswain of a longboat
- Poop: the higher part at the back of an old sailing ship
- Port (larboard): when facing forward, the left side of a ship
- Porthole (scuttles): a small window in the side of a ship or airplane
- Primage: fee paid to loaders for loading ship
- Promenade: deck the upper area of a ship where people walk for pleasure
- Propeller: a piece of equipment with blades that spin, used for moving a ship or aircraft
- Prow: the front of a ship or boat
- Purser: ship’s officer in charge of finances and passengers
- Quarterdeck: part of ship’s deck set aside by captain for ceremonial functions OR the back part of a ship’s upper deck, where the officers often live
- Quartering: sailing nearly before the wind
- Rake: the inclination of a mast or another part of a ship
- Ratline: small rope forming a rung of a rope ladder on a ship
- Reef: to reduce area of a sail by rolling or folding part of it
- Reeve: to pass a rope through a ring
- Rigging: the ropes and chains used for supporting a ship’s sails and masts
- Roach: curved cut in edge of sail for preventing chafing
- Roband: piece of yarn used to fasten a sail to a spar
- Rostrum: spike on prow of warship for ramming
- Rowlock: contrivance serving as a fulcrum for an oar
- Royal: small sail on royal mast just above topgallant sail
- Rudder: a flat piece of wood or other material at the back of a boat or airplane that is moved to change the direction of travel
- Sail: a large piece of strong cloth attached to a tall pole on a boat, used for catching wind to move the boat across water
- Saloon: a big room on a ship where passengers can sit together and talk, play games, etc.
- Scud: to sail swiftly before a gale
- Scupper: hole allowing water to drain from ship’s deck
- Scuttlebutt: cask of drinking water aboard a ship; rumor, idle gossip
- Sheer: fore-and-aft curvature of a ship from bow to stern
- Sheet: on a sailboat, the rope that is used for controlling the sail
- Shrouds: ropes supporting the mast of a ship
- Sickbay: a room where sick people go to rest and get medical treatment on a ship
- Side: the edge of a boat
- Sidelight: colored lights on side of a ship under way at night
- Skeg: part of ship connecting the keel with the bottom of the rudderpost
- Skysail: sail above the royal sail
- Skyscraper: triangular sail on a ship above the royal
- Slipway: ramp sloping into water for supporting a ship
- Snotty: naval midshipman
- Spanker: sail on the mast nearest the stern of a square-rigged ship
- Spar: any ship’s mast, boom, yard, or gaff
- Spinnaker: an extra sail sometimes put on the front of a boat used for racing OR a large triangular sail opposite the mainsail
- Spirketting: inside planking between ports and waterways of a ship
- Sponson: platform jutting from ship’s deck for gun or wheel
 Sprit: spar crossing a fore-and-aft sail diagonally
Sprit: spar crossing a fore-and-aft sail diagonally- Spritsail: sail extended by a sprit
- Starboard when facing forward, the right side of a ship
- Starbolins: sailors of the starboard watch
- Stay: large rope used to support a mast
- Staysail: fore-and-aft sail hoisted on a stay
- Steerage: the part of a passenger ship in which people who had the most inexpensive tickets traveled
- Steeve: to set a ship’s bowsprit at an upward inclination
- Stemson: supporting timber of a ship
- Stern: back part of a ship
- Sternpost: main member at stern of a ship extending from keel to deck
- Sternway: movement of a ship backwards
- Stevedore: dock worker who loads and unloads ships
- Stokehold: ship’s furnace chamber
- Stowage: space for storing things in a boat or vehicle
- Strake: continuous band of plates on side of a ship
- Stunsail: light auxiliary sail to the side of principal sails
- Sun deck: an open area on a ship where you can enjoy the sun
- Supercargo: ship’s official in charge of business affairs
- Superstructure: the part of a ship that is above the main deck
- Taffrail: rail round the stern of a ship
- Thole: pin in the side of a boat to keep oar in place
- Thwart: a seat across the middle of a rowboat
- Tiller: handle or lever for turning a ship’s rudder
- Timberhead: top end of ship’s timber used above the gunwale
- Timenoguy: rope stretched from place to place in a ship
- Topgallant: mast or sail above the topmast and below the royal mast
- Topmast: ship’s mast above the lower mast
- Topsail: ship’s sail above the lowermost sail
- Topside: on or relating to the deck of a ship
- Transship: to transfer from one ship to another
- Transire: ship’s customs warrant for clearing goods
- Transom: transverse timbers attached to ship’s sternpost
- Treenail: long wooden pin used to fix planks of ship to the timbers
- Trice: to haul in and lash secure a sail with a small rope
- Trunnel: wooden shipbuilding peg used for fastening timbers
- Trysail: ship’s sail bent to a gaff and hoisted on a lower mast
- Tuck: part of ship where ends of lower planks meet under the stern
- Turret: a high part on a military ship or vehicle where guns are attached. You can turn it in order to shoot the guns in any direction.
- Turtleback: structure over ship’s bows or stern
- Unreeve: to withdraw a rope from an opening
- Waist: the central part of a ship or an airplane
- Walty: inclined to tip over or lean
- Wardroom: a room on a warship used by all the officers except for the captain
- Washboard: broad thin plank along ship’s gunwale to keep out sea water
 Watching: fully afloat
Watching: fully afloat- Waterline: the highest point where water touches the side of a boat
- Waveson: goods floating on the sea after a shipwreck
- Wear: to turn a ship’s stern to windward to alter its course
- Weatherboard: weather side of a ship
- Weatherly: able to sail close to the wind with little leeway
- Wheelhouse: a small room on a boat where the wheel and other controls are
- Whipstaff: vertical lever controlling ship’s rudder
- Windbound: hindered from sailing by contrary winds
- Windlass: winch used to raise a ship’s anchor
- Yard: tapering spar attached to ship’s mast to spread the head of a square sail
- Yardarm: either end of the yard of a square-rigged ship
Ship Template
Name of Ship: What the ship’s name is.
Type of ship: See here for a list of types of ships.
Size of Ship: the ship’s dimensions, if other than standard for its type.
Crew: Number of crew on board, and positions.
Crew Racial Makeup: What races are aboard the ship, if applicable.
Armor: the defensive capabilities of the ship, if applicable.
Armory: the offensive capabilities of the ship, i.e. what types of canons the ship holds and the sizes, if applicable.
Cargo: What the ship’s carrying, if applicable.
Propulsion: how it gets around: e.g. wind, steam, magic, oars, etc.
Maneuverability: how easily it gets around.
Blank Ship Template
Name of Ship:
Type of ship:
Size of Ship:
Crew:
Crew Racial Makeup:
Armor:
Armory:
Cargo:
Propulsion:
Maneuverability:
D30 Ship-based / Water Hazards
- Calm weather: the ship can’t go anywhere because there’s not a breeze to catch the sails
- Lack of visibility: If you can’t see where you’re going, the ship can run aground, or you can get lost.
- Hot metal: The sun beating down on metal objects can cause them to become too hot to handle.
- Scurvy: caused by lack of nutrients. Causes teeth to fall out
- Airy Water: This is an area of air that is filled with bubbles that allow things that are able to breathe water are able to survive in. Most fish will avoid these areas.
- Slippery Surfaces: The surface of a deck. This includes such things as the ropes, wood and metal surfaces
- Coral Scratch: Injuries from coral don’t heal normally, and must be healed either magically or takes .
- Sunburn: The characters are exposed to sunlight for many hours may get burned by the sun
- Seasickness: The characters get ill due to the motion of the sea
- Poisonous marine life: catching and eating this marine life is bad for characters, causes them to be poisoned
- No sea legs: The character is unsteady on his/her feet on a boat
- Boiling Water: Underwater volcanic vents boil water in the vicinity where they form.
- Venomous marine life: contact with this marine life is similar to the sting of an insect.
- Airless Water: an area of water that is devoid of air, a dead zone, devoid of fish.
- Lost Islands: places that don’t show up on the maps. What’s on these lost islands, or why they’re there is up to the DMs.
- Whirlpool: a body of swirling water produced by the meeting of opposing currents.
- Inability to swim: the character either naturally has no ability to swim or has lost it for some reason (think the Devil Fruit users in One Piece)
- Other Ships Attack: Another ship attacks the ship the characters are on
- Man Overboard: A person gets swept or falls overboard for some reason
- Violent seas: the ship is being tossed about by bad weather / choppy seas. This includes such hazards as waterspouts.
- Monster attack: a giant squid, shark, or other monster attacks the ship
- Underwater caves: a water filled cave must be navigated by the ship (or by an underwater expedition team)
- Depth: the water is too deep to dive, either by the ship or characters. Even with rebreathers and SCUBA gear, characters can suffer “the bends”
- Drowning: not being able to breathe underwater or having magics that allow one to do so expire
- Hypothermia: characters get bad effects from swimming/ being exposed to cold weather/ water
- Currents: boats can be swept away by strong currents
 Fire: a fire breaks out on the ship and those aboard need to find out how to put it out (if it *can* be put out)
Fire: a fire breaks out on the ship and those aboard need to find out how to put it out (if it *can* be put out)- Radiation: the ship is nuclear and has a radiation leak
- Shipwreck: the ship sinks and those aboard need to get off it
- Defiling Sludge: This sludge is a potential hazard games where all sorts of evil runs amuck. It is the remnants of vile magic that have flowed into the sea. Momentary contact with it weakens an object and continuous contact with it quickly dissolves it. It is corrosive to the flesh. The sludge can’t be easily destroyed, only driven away with such things as crystal and jade. This is the stuff that shows up in “The Pirates of Dark Water.”
Now you have some vocabulary, a template to use your ships, and some ship and water based hazards, you’ll be more equipped to send your player characters on a voyage to use ships as a dungeon.
Thanks for reading!



